
What is forced induction?
Forced induction has built a reputation for being the ultimate addition to a vehicle when chasing significant power increases. Today, forced induction can be found more and more in passenger vehicles, as it can improve efficiency while preserving power and torque.
But what exactly is forced induction? In this article, we’ll go over the pros and cons of forced induction systems, as well as why they’ve taken such a massive hold on the automotive industry.
What is forced induction?
When you get down to it, engines are air pumps. Combustion is achieved by igniting a mixture of air and fuel, and the energy from the combustion sends power to the wheels of the car. The more air and fuel that can be introduced into the combustion stage, the more power can be produced.
Adding more fuel is relatively easy. In modern cars, fuel pumps and injectors control the flow of fuel. Air flow to the engine is limited by the engine’s suction and atmospheric ambient air pressure. Engines without forced induction are considered naturally aspirated.
Forced induction allows more air to be “forced” into the engine at a higher than atmospheric pressure.
This means that increasing the amount of air pushed into the engine will result in more powerful combustion and a considerable increase in power. By extracting more power from combustion, small engines are able to run more efficiently while still making solid horsepower numbers, and performance engines can increase power significantly.
At one time, forced induction was a technology limited to high-performance sports cars, racing applications, aviation, and heavy-duty diesel trucks. While most vehicles on the road are still naturally aspirated, more and more vehicles, from commuter cars to sports bikes, are getting boosted.
Type of forced induction
Forced induction is achieved with two main technologies; turbochargers and superchargers. Although they accomplish the same thing, the way these devices pressurize air is different.
superchargers
As the original form of forced induction, superchargers saw their first adoption in aircraft and automobile engines in the 1920s and 1930s. Race cars and warplanes were the only common use cases for to forced induction during the first half of the 20th century, but as designs and development progressed, they eventually became a method widely used in consumer sports cars, luxury vehicles, and the American muscle scene.

The defining characteristic of superchargers is their belt-driven designs, meaning they are powered by the output of the engine itself. A drive belt runs off the engine, turning the compressor with it. Superchargers are engine-driven air compressors, which use an impeller to create pressure and force large amounts of air into the engine. The faster the engine spins, the more pressure the air will get.
Because superchargers are driven by the engine, they create a very linear increase in boost pressure. Supercharged engines do not have the “spiky” nature of turbochargers, which will be discussed later in this article.
This is also one of the main drawbacks of the supercharger. Because they rely on the energy produced by the engine, superchargers are “parasites,” meaning they leach energy from the engine to create boost. This means that superchargers are significantly less efficient than their turbocharged counterparts.
Turbocharger
Similar to superchargers, turbochargers (commonly called turbos) were first used in aviation and even marine applications before reaching consumer vehicles.
Turbos have become the most common form of forced induction in recent years. Although they serve the same purpose as superchargers, the method in which they do so is very different.
Turbocharging uses what would normally be spent exhaust gases to spin a turbine to create pressure, rather than being belt-driven. As a result, turbochargers can produce boost without parasitic extraction.
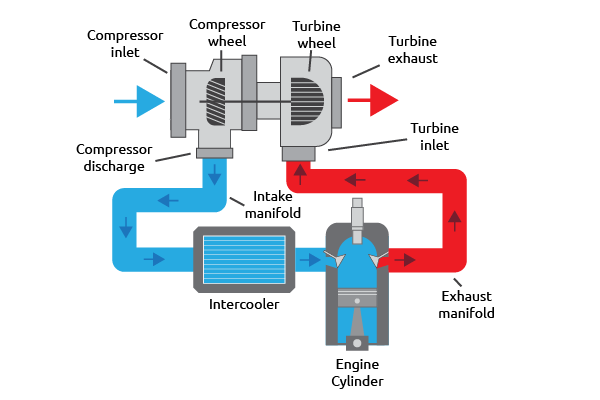
However, this reliance on exhaust also comes with its biggest drawback: turbo lag. A turbocharger’s power delivery is neither immediate nor linear, as the exhaust gases must first wind the turbine. This sluggish feeling is commonly called turbo lag.
The problem of turbo lag has been partially mitigated by advances in turbocharger designs, but the problem remains one of the biggest drawbacks of turbochargers.
Why forced induction?
Although force induction started in racing, industrial, and military applications, as we moved on, it has gained popularity among automakers over the years. Even the new Volkswagen Jetta and Chevrolet Trax make use of technology that was once reserved for the most advanced vehicles of the era.
It turns out that forced induction is useful for more than just making fast cars. While turbos don’t directly increase fuel economy, they do allow manufacturers to squeeze more power out of small, efficient engines. Vehicles that once required a V8 can now use a turbocharged 4- or 6-cylinder, meaning SUVs and trucks can use them to increase fuel economy while maintaining or even increasing horsepower figures.
Advances in turbocharger designs have made them considerably more reliable and efficient than before, making them practical in circumstances they may not have been 15 years ago.
Turbocharger vs. Supercharger: Which is better?
The two main forms of forced induction have their advantages and disadvantages. Superchargers provide instant increases in power, while turbos suffer from lag as the turbine spins at full speed. However, turbochargers gain in efficiency, since they do not consume their power from the engine itself.
Superchargers tend to be the more reliable of the two, as they are generally simpler designs than turbos with fewer components to fail over time. That said, turbochargers have come a long way in terms of reliability.
While neither is a bad choice, turbochargers have largely gained popularity among manufacturers due to their fuel-efficient designs and non-parasitic nature. The question of which one is best for you depends entirely on personal preference and the type of vehicle you are buying.
Turbo and Supercharger services at Alex’s Autohaus
If you have a forced induction vehicle or want to have it installed in your vehicle, the performance experts at Alex’s Autohaus can take care of you! Our ASE certified technicians have extensive experience in the inspection, maintenance and repair of forced induction systems. Call or schedule an appointment today on our website.


