Internal combustion engines are essential components of modern vehicles that provide the power to propel a car. All that is about to change once electrified vehicles take over. We’re still a few years away from that, and ICE engines still power most of the auto industry, and may never go away. And as they’ve proven over the years, car engines are complex and intricate machines that can experience a wide range of problems over time, from minor issues to major failures.
An engine has many moving parts that can develop problems and is one aspect of the car that you cannot compromise on. Understanding why engines develop problems can help car owners take proactive steps to maintain their vehicles and avoid potential problems like engine overheating, which can cause permanent engine damage if left untreated. Other signs of a problematic car engine can include low oil pressure, strange noises and reduced performance. Here are potential car engine problems you can help prevent through regular maintenance and inspections.
10 Blocked engine radiators
Engines generate a lot of heat and require a cooling mechanism. We’ve had several great cars with air-cooled engines, such as the classic Porsche 911 Turbos. But, most modern vehicles come with liquid cooling, which is more efficient than air cooling in terms of cooling performance. The radiator removes heat from the engine coolant and dissipates it to the surrounding air.
Old engine coolant that is not kept clean over time can fill engine radiators with unwanted sediment and deposits. Also, over time, debris such as dirt, leaves and insects can build up on the radiator fins, reducing airflow and causing the engine to overheat.
9 Engine coolant leak
Coolant leaks are another common engine problem in the cooling department, in addition to blocked radiators. The coolant circulates in the engine and absorbs heat before being transferred to the radiator, where it cools and repeats the loop.
Leaking engine coolant can cause a number of problems, including engine overheating, which will lead to engine damage if not addressed quickly. It is one of the easiest problems to diagnose, and if it is consistently low, it is a clear sign that there is a failure in the cooling system.
8 Engine ignition error
An engine misfire occurs when one or more cylinders do not ignite the air-fuel mixture properly and the engine suddenly loses power. Some noticeable symptoms include rough idling or reduced engine performance, slower acceleration, jerking or vibration, or engine stalling.
Other symptoms may include black smoke from the exhaust or a flashing check engine light. It can indicate a faulty ignition system with a problem emanating from the crankshaft position sensor, ignition coil packs, spark plug boot, control circuit, emissions equipment problems, or spark plug .
7 Clogged fuel injectors
Fuel injectors play a crucial role in delivering fuel to the engine. They atomize the fuel and spray it into the combustion chamber, igniting it to power the engine, but they can become clogged with dirt, debris and other contaminants.
Some of the common symptoms of clogged fuel injectors include reduced engine performance, poor fuel economy, rough idling, or a misfiring engine. You should clean your fuel injectors every 30,000 miles.
6 Oil pump failure
Lubrication is one of the most critical aspects of an engine, with many moving parts that rub against each other. The engine needs sufficient lubrication between these parts to minimize unnecessary friction within the engine to prevent overheating and excessive wear.
While regular oil changes are essential, you also need to watch out for oil pump failure, which can be a life-threatening problem for any engine. Broken oil pumps will deprive the engine of the necessary lubrication.
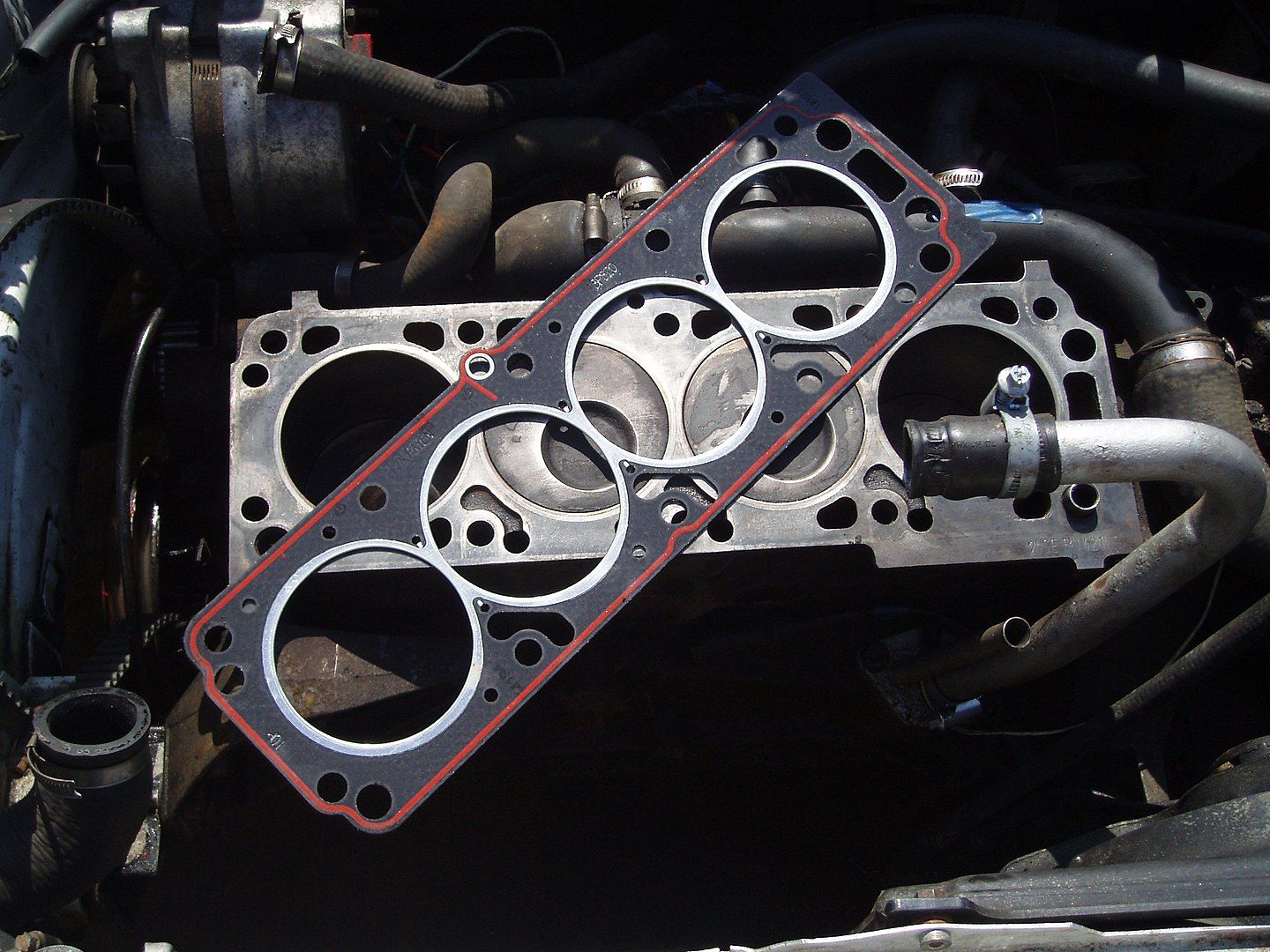
5 Blown head gasket
The car engine runs in extreme conditions and intense heat, which can sometimes get out of control and cause things to explode. One of the most common culprits is the head gasket, which cushions the pistons and cylinders of the cylinder head check valves, spark plugs and camshafts.
The head gasket seals the cylinder firing pressure and prevents coolant and engine oil from escaping into the cylinders and out. Common symptoms of a blown head gasket include overheating, loss of engine power, white smoke from the exhaust, milky oil, and engine misfires.
4 Worn combustion parts
Over time, the combustion parts of the combustion chamber, where air and fuel mix to power the engine, such as pistons, cylinders, piston rings, valves and spark plugs, can wear out and cause a series of problems.
Piston rings are the usual culprits of wear in the combustion chamber. They are small and simple, but crucial parts that play an important role in the indispensable precision of engine function. They help seal the chamber, lubricate the cylinder walls and allow heat transfer. Symptoms include rough engine running, blue smoke from the exhaust, loss of engine oil, and reduced efficiency.
3 Inadequate fuel and air compression
The engine needs fuel and air compression to generate power, and poor compression is a recipe for disaster, as the engine operates entirely on the principle of compression. A car with low or no compression on all cylinders will not start, or may misfire and misfire when some cylinders experience this problem. Common causes include blown head gaskets, worn pistons, broken timing belts, or faulty valves.
2 Damaged oxygen sensors
Modern cars have many sensors that provide essential data to the engine control unit to ensure that the engine is running at maximum efficiency. Some of the most common and crucial sensors include oxygen sensor, mass air flow sensor, throttle position sensor, engine coolant temperature sensor, knock sensor, speed sensor and much more.
A faulty oxygen sensor alters the air-fuel mixture and causes increased fuel usage, rough idling, poor acceleration, engine misfires, or an illuminated check engine light.
1 Excess combustion pressure
Excess combustion pressure is a common engine problem that occurs when the air/fuel mixture in the engine cylinder is ignited too early or too late, causing the combustion pressure to increase beyond the safe limit. Carbon buildup can cause the exhaust system to clog, which reduces the space available for the air/fuel mixture, thereby increasing combustion pressure.
Also, using the wrong type of fuel can lead to premature ignition, while timing problems or misalignment of the engine can lead to combustion at the wrong time, causing excess pressure and damage to the engine Symptoms include knocking or pinging sounds, overheating, or reduced performance.
Sources: MotorTrend, Hagerty